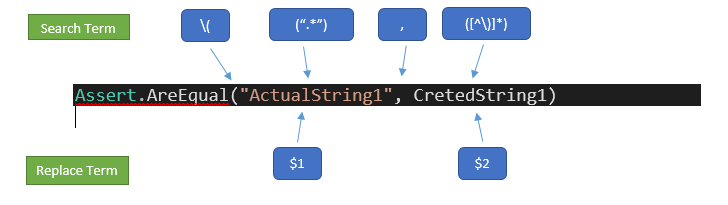
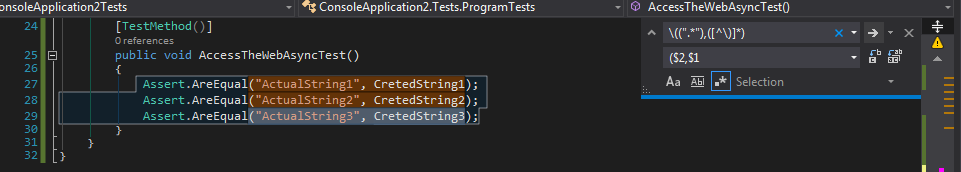
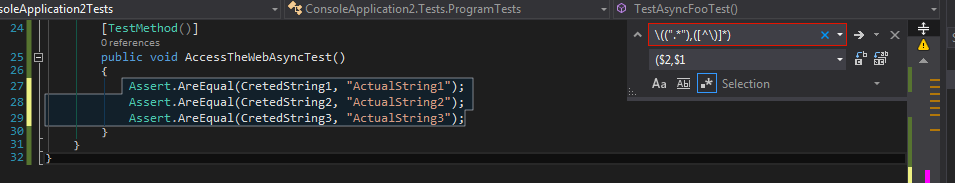
Git Basic Commands
Introduction to Git
Git, a version control created by Linus, creator of Linux. It was created for managing contributions to linux code base. This post is covering some of the basic commands which used regularly.
Git Terms
Branch : Branch is to start a new line of development. It will be independent of the main and act as new workspace. It will allow the developer to move in new working directory without messing the main code.
Remote : A remote repository is hosted in internet and we keep our project copy there. It will act as a center repository for the project and different local repositories will push code to the remote.$ git remote - to list all the remotes.
Upstream : It is used to refer the original repository we used to fork. While we fork a repository, it will not set the upstream by default. We must configure a upstream repository in Git to sync changes made in the original repository.
Forking : Forking gives a way to create a copy of server side repository from the original server repository. It will act as the remote for the local repository and allow the contributor to have a public repository to share. Contributor will have both private local one and public server-side one.
Git Commands
- Forking the repository
In the top-right corner of the page, click Fork. Clicking on the fork button from project page will create a forked project under your account. - Cloning the forked repository
$ git clone https://github.com/user/awesome.git - Setting up upstream
$ git remote add upstream https://github.com/original_author/awesome.git
After setting up the upstream, we can sync the upstream to get changes made in the original repository. - Creating a new branch
$ git checkout -b MyNewBranch- This will create a new branch and checkout it. - Committing changes to the new branch
$ git push origin MyNewBranch - Deleting the branch after merging
$ git branch -D MyNewBranch- This will delete the branch even if we did not merge or rebase it. - Pruning all branches
$ git remote prune origin - Fetching changes from the upstream
To get the latest changes made in the original repository, we can fetch it from upstream.$ git fetch upstream - Merging our master with upstream
$ git merge upstream/master